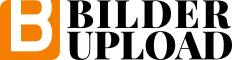9.3. What Is IP Filtering?
IP filtering is simply a mechanism that decides which types of IP
datagrams will be processed normally and which will be discarded. By
discarded we mean that the datagram is deleted
and completely ignored, as if it had never been received. You can
apply many different sorts of criteria to determine which datagrams
you wish to filter; some examples of these are:
Protocol type: TCP, UDP, ICMP, number (for TCP/UPD)Datagram type: SYN/ACK, data, ICMP Echo Request, gram source address: where it came fromDatagram destination address: where it is going to
It is important to understand at this point that IP filtering is a
network layer facility. This means it doesn’t understand anything
about the application using the network connections, only about the
connections themselves. For example, you may deny users access to your
internal network on the default telnet port, but if you rely on IP
filtering alone, you can’t stop them from using the telnet program
with a port that you do allow to pass trhough your firewall. You can prevent
this sort of problem by using proxy servers for each service that you
allow across your firewall. The proxy servers understand the
application they were designed to proxy and can therefore prevent
abuses, such as using the telnet program to get past a firewall by
using the World Wide Web port. If your firewall supports a World Wide
Web proxy, their telnet connection will always be answered by the
proxy and will allow only HTTP requests to pass. A large number of
proxy-server programs exist. Some are free software and many others
are commercial products. The Firewall-HOWTO discusses one popular set
of these, but they are beyond the scope of this IP filtering ruleset is made up of many combinations of the criteria
listed previously. For example, let’s imagine that you wanted to allow World
Wide Web users within the Virtual Brewery network to have no access to the
Internet except to use other sites’ web servers. You would configure your
firewall
to allow forwarding of:
datagrams with a source address on Virtual Brewery network, a destination
address of anywhere, and with a destination port of 80 (WWW)datagrams with a destination address of Virtual Brewery network and a
source port of 80 (WWW) from a source address of anywhere
Note that we’ve used two rules here. We have to allow our data to go out,
but also the corresponding reply data to come back in. In practice, as we’ll
see shortly, Linux simplifies this and allows us to specify this in one
command.
Port Filter – Block Risky Network Ports With BrowseControl | CurrentWare
The Tennessee College of Applied Technology (TCAT) is one of the best technological educational institutions in the Tennessee area. To keep delivering a cutting-edge learning experience, TCAT Crump knew that they needed to integrate online resources into their curriculums and teaching methods. But allowing internet access into a network is not without its risks. As an information technology instructor, Gabriel Alvarado is adamant that educational institutions need to defend against unauthorized access to personal information belonging to pupils, parents, or staff. Gabriel knew that restricting internet access with internet blocking software was essential for protecting their students and network against web-based threats. In addition to improving internet security, BrowseControl provided TCAT students with an optimal educational experience by blocking distracting websites during class hours and preventing bandwidth hogs from impacting the performance of the network. BrowseControl’s convenient remote installation options and central management console made it the best internet filtering software for TCAT as they could deploy the software during the school term rather than having to wait until the holidays. Staff and user accounts could be readily distinguished, allowing web filtering policies to be customized to the needs of each group.

IP Address filtering – Kemp
IP Address Filtering is a mechanism that determines what to do with network data packets based on their sender or destination address. In either case the packet is inspected by a network router or firewall and based on rules set by an administrator, the packet is passed on to next node on the network. If the rules say that packets with a particular address should not be sent on, then the packet is simply ignored. Which means it is not propagated via the current network route. It may still be delivered via another network route, as Internet traffic can follow multiple paths to destination.
Frequently Asked Questions about ip and port filtering
What is IP filtering and how is it used?
IP filtering lets you control what IP traffic will be allowed into and out of your network. Basically, it protects your network by filtering packets according to the rules that you define. NAT, allows you to hide your unregistered private IP addresses behind a set of registered IP addresses.
What is port filtering in router?
port filtering is when a router monitors the destination ports of the tcp/udp and/or other port-based network protocol packets that pass through it. with port filtering you can have the router block packets that are heading to a certain port or block some packets based on their content.Aug 14, 2001
What is port filtering?
Port filtering is the practice of allowing or blocking (opening/closing) network packets into or out of a device or the network based on their port number.